Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
When I first started exploring the world of robotics, one thing became very clear — robotics engineers don’t just build machines. They design intelligent systems that sense, think, and act. From industrial automation and autonomous vehicles to surgical robots and space exploration, robotics engineers are shaping how humans and machines collaborate.
If you enjoy mathematics, physics, coding, problem-solving, and creating real-world impact through technology, understanding how to become a robotics engineer can open doors to one of the most future-proof and globally relevant careers.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through how to become a robotics engineer step-by-step — from education and certifications to skills, course timelines, salary potential, and an industry-ready career roadmap. By the end, you’ll clearly understand whether robotics engineering aligns with your interests, strengths, and long-term goals.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Robotics Engineer
Robotics engineering is multidisciplinary, innovation-driven, and rapidly evolving with advances in AI, IoT, automation, and Industry 4.0. Your role varies depending on the industry, specialization, and organisation.
Key Responsibilities of a Robotics Engineer
Robotics engineers work at the intersection of hardware, software, and intelligence. Their core responsibilities include:
- Designing, building, and testing robotic systems and automation solutions
- Developing control algorithms for robotic movement and decision-making
- Programming robots using languages like Python, C++, and ROS
- Integrating sensors, actuators, and embedded systems
- Working on AI, machine learning, and computer vision for robotics
- Troubleshooting hardware and software issues in robotic systems
- Collaborating with mechanical, electrical, and software teams
- Optimising robots for efficiency, safety, and scalability
- Staying updated with robotics standards, tools, and technologies
- Deploying robots in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, or research environments
Work Environment of a Robotics Engineer
A robotics engineer can work across multiple professional environments:
1. Manufacturing & Industrial Automation
- Robotics for assembly lines and smart factories
- High demand in automotive, electronics, and FMCG sectors
- Exposure to Industry 4.0 systems
2. Research & Development (R&D)
- Advanced robotics, AI-driven systems, and innovation labs
- Universities, defence labs, and private research firms
3. Startups & Product Companies
- Fast-paced innovation
- Hands-on work across hardware and software
- Exposure to autonomous systems and emerging tech
4. Healthcare & Medical Robotics
- Surgical robots, rehabilitation devices, assistive technologies
- Strong growth and ethical impact
5. Defence, Space & Autonomous Systems
- Drones, unmanned vehicles, robotics for space missions
- High-security and advanced engineering roles
Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications
Understanding how to become a robotics engineer starts with choosing the right academic and technical pathway. Robotics allows multiple entry routes, especially when combined with strong skill-building.
Complete Education & Certification Roadmap for Becoming a Robotics Engineer
Robotics courses after 12th in India are commonly pursued through engineering degrees, diplomas, or integrated programs combining robotics, AI, and automation.

Typical Skills & Personal Qualities You’ll Need
One thing I’ve consistently seen in successful robotics engineers is this — degrees open doors, but skills determine how far you go. Robotics is not just about knowing theory; it’s about how you think, learn, and solve problems when machines don’t behave as expected.
The right mix of technical capability and personal qualities is what turns a learner into a reliable, industry-ready robotics engineer.
Technical Skills Every Robotics Engineer Must Build
- Strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and linear algebra
- Programming skills (Python, C++, MATLAB)
- Robot Operating System (ROS)
- Embedded systems and microcontrollers
- Sensors, actuators, and control systems
- AI, machine learning, and computer vision basics
- CAD tools and mechanical design understanding
- Simulation tools (Gazebo, MATLAB Simulink)
Soft Skills That Shape a Successful Robotics Engineer
- Analytical and systems-thinking mindset
- Curiosity and continuous learning attitude
- Team collaboration across disciplines
- Precision, patience, and attention to detail
- Ethical awareness and safety focus
Not sure whether these skills genuinely match your thinking style—or just sound good on paper?

Career Progression: From Beginner to Industry-Ready Robotics Engineer
When students ask me how to become a robotics engineer, the biggest confusion is not about courses — it’s about what comes after each stage. Robotics careers don’t grow overnight; they evolve through structured learning, hands-on experience, and smart specialisation choices.
This progression shows how you move from a beginner exploring robotics to an industry-ready engineer trusted with real-world systems and innovation.
1. Career Path After Class 12 / Graduation
- a) Entry-Level Roles
- Robotics Engineer Trainee
- Automation Engineer
- Embedded Systems Engineer
- Junior AI / Robotics Developer
- b) Choose Between 4 Main Routes
- Core robotics engineering roles
- AI + robotics specialization
- Industrial automation & PLC pathway
- Research & higher studies
2. Growth Opportunities at Each Stage
After Certifications & Early Experience
- Robotics Engineer
- Automation Specialist
- ROS Developer
With Experience (5–8 Years)
- Senior Robotics Engineer
- Robotics System Architect
- Technical Lead / Product Manager
Advanced Growth Tracks
- Autonomous vehicles & drones
- Medical & surgical robotics
- AI-driven intelligent systems
- Robotics entrepreneurship & startups
Salary Expectations
Average Income of a Robotics Engineer in India
- Entry-Level
₹4–8 lakhs per year - Mid-Level (3–6 Years)
₹10–20 lakhs per year - Experienced Robotics Engineer / Lead Roles
₹25–50 lakhs+ annually - Global Roles, R&D & Niche Expertise
₹1 crore+ potential with international exposure
Robotics engineer salary in India continues to rise due to automation, AI integration, and skill shortages.
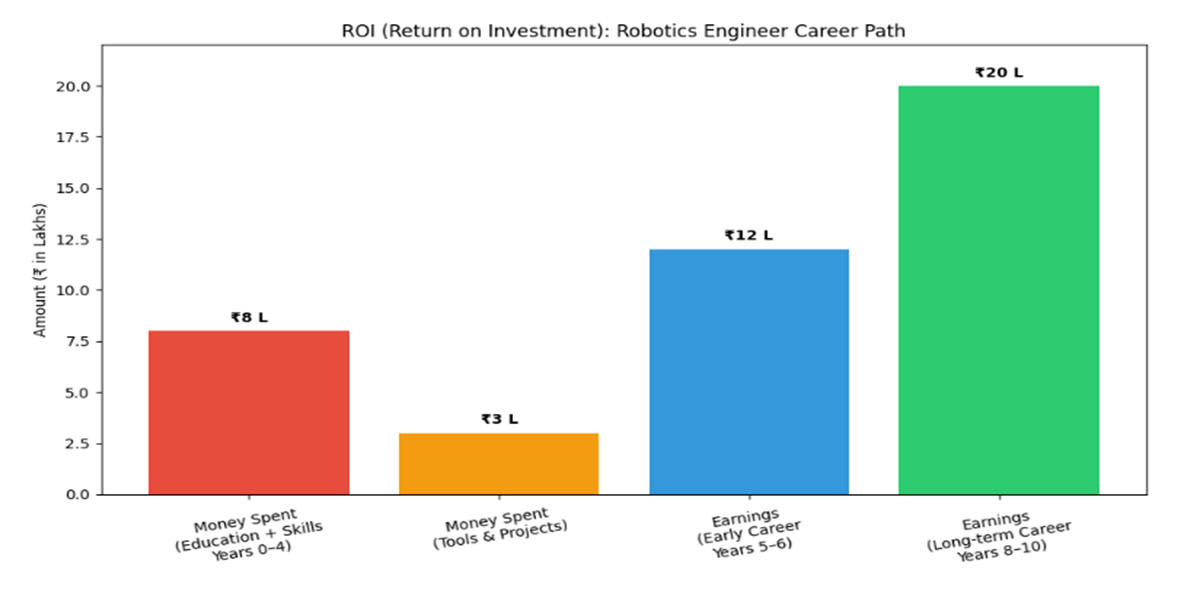
Understanding ROI and ROT in a Robotics Engineering Career
ROI – Return on Investment
Total Initial Investment (Years 0–4)
Year 0–4: Education & Skill Building Phase
- Formal education (B.Tech / BE / Diploma / Certifications): ₹2–8 lakhs
- Tools, projects, labs, certifications, software & hardware kits: ₹1–3 lakhs
🔹 Total Investment Range: ₹3–11 lakhs
This investment is usually spread across 4 years (engineering degree) or 3–5 years depending on the chosen pathway.
Earnings & Payback Timeline (Post Graduation)
Year 5 – Entry-Level Robotics Engineer
- Average annual salary: ₹4–8 lakhs
- Approx. savings toward ROI: ₹2–4 lakhs
Year 6 – Skill Consolidation Phase
- Average annual salary: ₹6–10 lakhs
- Approx. savings toward ROI: ₹3–5 lakhs
Year 7 – Industry-Ready Engineer
- Average annual salary: ₹10–15 lakhs
- Approx. savings toward ROI: ₹5–7 lakhs
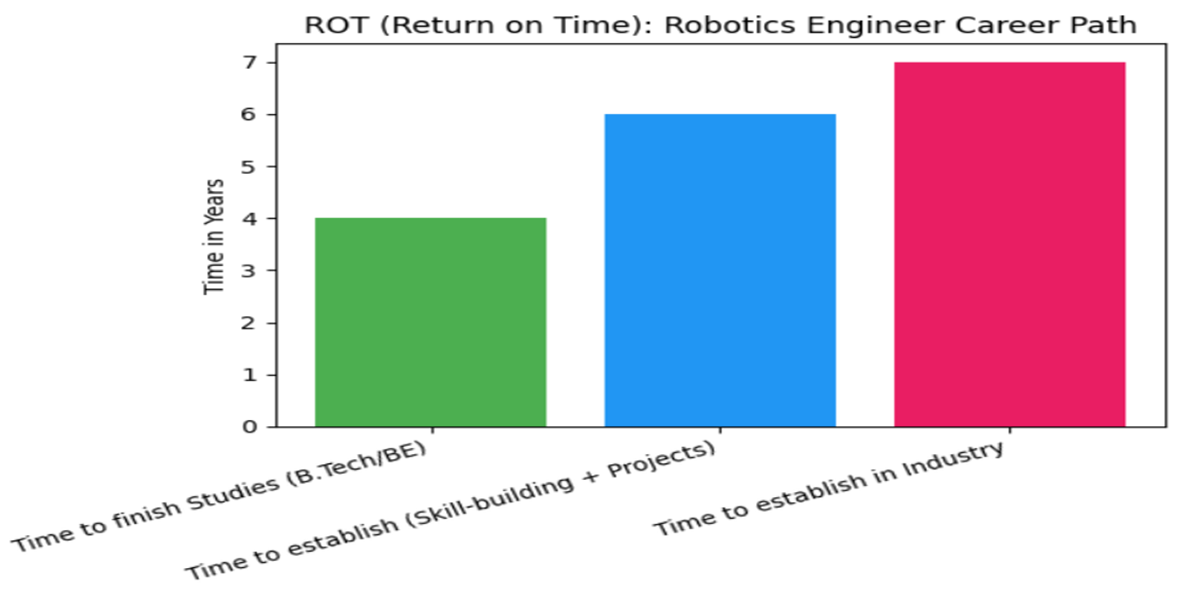
ROT – Return on Time
Skill-building Phase (2–4 years):
- Includes: Completing a degree (B.Tech / BE), working on personal projects, certifications, learning core technical skills (mathematics, programming, robotics basics, AI, etc.).
- Timeframe: 2–4 years (depending on whether it’s a B.Tech or a diploma).
Industry Credibility Phase (4–6 years):
- Includes: Gaining hands-on experience in the industry, working on robotics projects, becoming proficient in using relevant technologies, and earning industry recognition.
- Timeframe: 4–6 years (typically includes 2–3 years post-degree for entry-level and mid-level work experience).
Long-term Leadership & Innovation Phase (after ~6 years):
- Includes: Establishing yourself in leadership roles such as Robotics System Architect or Technical Lead. Exploring innovation opportunities in fields like AI-driven robotics, autonomous vehicles, and robotics entrepreneurship.
- Timeframe: 6+ years (depending on the individual’s progress and career trajectory).
Conclusion: Is a Career as a Robotics Engineer Right for You?
Choosing how to become a robotics engineer means choosing a career rooted in innovation, problem-solving, and future technologies. If you enjoy building intelligent systems, working with hardware and software, and shaping how humans interact with machines, robotics offers immense growth and global relevance.
The robotics engineer scope in the future is vast — spanning automation, AI, healthcare, defence, space, and smart cities. With the right education, skills, and guidance, you can build a resilient and impactful engineering career.
Connect with our expert counsellors at NextMovez today and get a personalised robotics engineering career roadmap based on your strengths and aspirations.
Let’s turn your interest in robotics into a confident, industry-ready professional journey.
Resources and References
- Ministry of Education, Government of India (Engineering & Technical Education Framework)
https://www.education.gov.in - All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) – Approved Engineering & Robotics Programs
https://www.aicte-india.org - Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) – Robotics, AI & Automation Research Labs
https://www.iitsystem.ac.in - Robot Operating System (ROS) – Official Documentation & Learning Resources
https://www.ros.org - IEEE Robotics and Automation Society – Global Standards & Research
https://www.ieee-ras.org - Coursera – Robotics and AI Professional Certificate Programs
https://www.coursera.org/browse/information-technology/robotics - edX – Robotics, Automation & AI Courses from Global Universities
https://www.edx.org/learn/robotics - Udacity – Robotics Software Engineer Nanodegree
https://www.udacity.com/course/robotics-software-engineer–nd209