Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
Tech Meets Medicine: How to Become a Radiologist in the Age of AI & Innovation
The healthcare field is evolving rapidly, and one of the most exciting career paths today is becoming a radiologist. If you’ve ever found yourself wondering, “How can I become a radiologist?” — you’re not alone. With the growing advancements in technology, particularly AI, radiology is at the cutting edge of innovation in medicine. Radiologists play a critical role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment plans, and using imaging technology like X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and more to help doctors make life-saving decisions.
In my opinion, becoming a radiologist is much more than just reading images. It’s about developing a deep understanding of the human body, mastering complex imaging technologies, and continuously learning as the field evolves. Whether you’re fascinated by the mechanics of medical imaging or have a passion for helping patients through early detection of conditions, radiology offers a fulfilling career path. In India, the demand for radiologists is increasing, especially with advancements like AI and machine learning, which are reshaping the way we think about diagnostics.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through the journey of becoming a radiologist in India. We’ll talk about the education, skills, and qualifications you need, the exams to take, and the career opportunities available in radiology. Plus, I’ll share how you can navigate the future of radiology with AI and tech innovations — and why understanding these changes is essential for anyone looking to pursue this career.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Radiologist
When it comes to becoming a radiologist, your day-to-day responsibilities will be both exciting and ever-changing. From reviewing imaging scans in the morning to collaborating with doctors on treatment plans in the afternoon, radiology is a dynamic and intellectually stimulating field. It’s not just about looking at images; it’s about interpreting them to make crucial decisions that can impact the lives of patients.
In my experience, being a radiologist requires not only technical expertise but also the ability to think critically and communicate effectively with your healthcare team. According to the American College of Radiology, the primary responsibility of a radiologist is to accurately interpret medical images, which can help in diagnosing conditions ranging from bone fractures to complex cancers. But let me walk you through the key responsibilities of a radiologist and the kind of environment you can expect to work in.

Key Responsibilities of a Radiologist
Image Interpretation and Diagnosis
One of the most important tasks a radiologist does is reviewing medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, to detect abnormalities. Whether it’s identifying a tumor or detecting a fracture, radiologists must analyze the images carefully and accurately to provide diagnoses. This requires a deep understanding of human anatomy and medical conditions.
Collaboration with Physicians and Specialists
Radiologists don’t work in isolation. They play an essential role in a multidisciplinary healthcare team. Once a diagnosis is made, radiologists collaborate with doctors, surgeons, and oncologists to discuss the findings and suggest appropriate treatment plans. This requires excellent communication skills and a strong understanding of how imaging affects patient care.
Advancement in Medical Technology
Radiology is a field that’s deeply intertwined with cutting-edge technology. With the rise of AI and machine learning, radiologists now rely on advanced algorithms to assist in image interpretation. These innovations help improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. In fact, according to a study by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), AI has shown promise in assisting radiologists with tasks like detecting breast cancer and brain aneurysms. Understanding how to work with these technologies is becoming an integral part of the job.
Patient Interaction and Safety
Although radiologists work behind the scenes, they still need to ensure that patients are comfortable and understand the procedures. From explaining the imaging process to ensuring patient safety (especially regarding radiation exposure), radiologists must prioritize the well-being of those they are diagnosing.
Specialization in Radiology
As you progress in your career, you can specialize in various areas of radiology, including but not limited to:
- Interventional Radiology: Using imaging to guide surgical procedures like biopsies and stent placements.
- Pediatric Radiology: Specializing in imaging for children.
- Neuroradiology: Focused on the brain, spine, and nervous system.
Oncologic Radiology: Specializing in imaging cancer and guiding treatment.
Work Environment for Radiologists
Whether you work in a hospital, a diagnostic center, or a private clinic, the environment you find yourself in will largely depend on your role and the type of facility. Here’s a closer look at where you might work:
Hospitals and Medical Centers
Radiologists are in high demand in hospitals and medical centers. Here, you’ll likely work in imaging departments, interpreting a variety of scans from different specialties. The pace can be fast, especially in emergency or trauma settings, and the workload might be heavy, but the sense of impact on patient outcomes is significant.
Private Practices and Diagnostic Centers
In a more specialized or private setting, radiologists tend to have a more controlled environment, focusing on specific imaging services. The hours might be more predictable, but the work remains just as critical. Radiologists in this setting often work closely with referring doctors to provide tailored imaging services for their patients.
Academic and Research Institutions
For those interested in teaching or conducting research, academic institutions offer the opportunity to advance the field of radiology. Here, radiologists not only diagnose but also participate in research, shaping the future of medical imaging. Working in academia often involves a blend of clinical practice and teaching, providing a more balanced career option.
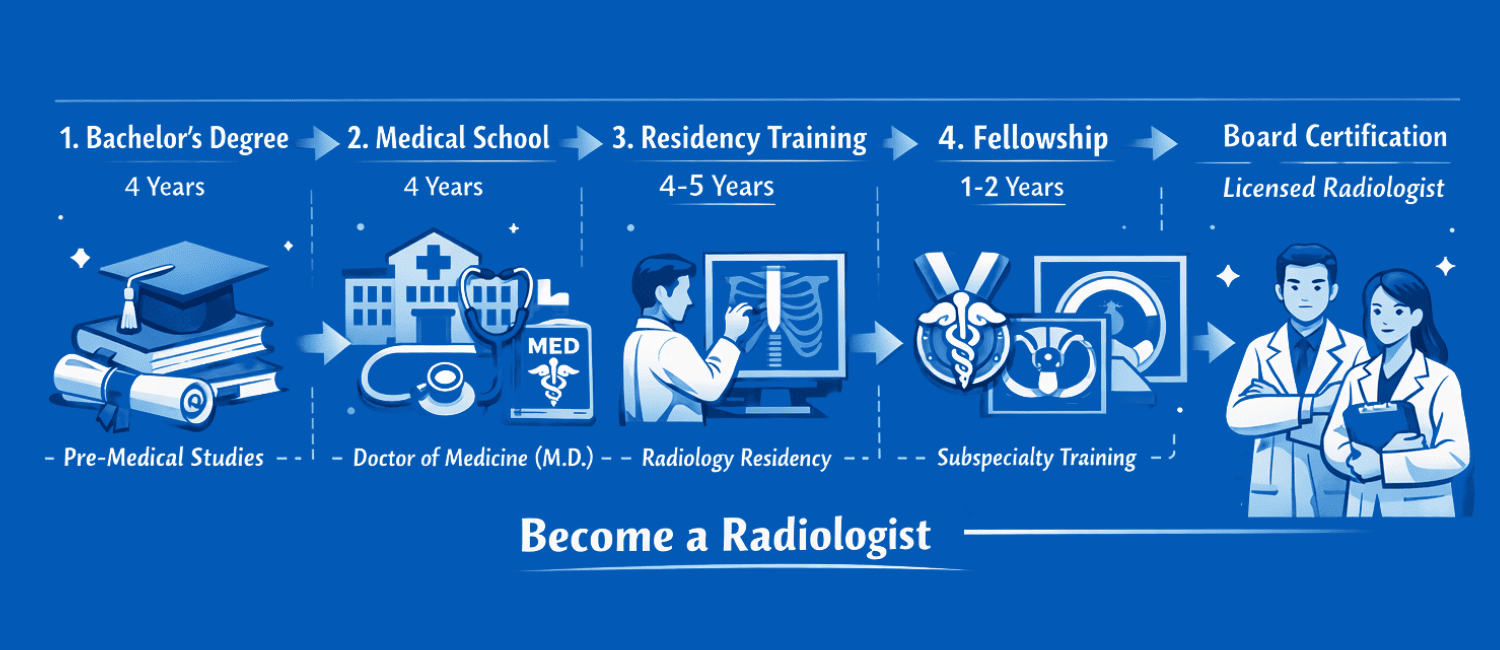
Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications to Become a Radiologist
Becoming a radiologist is a rewarding and challenging journey that requires a blend of academic excellence, technical skills, and hands-on clinical experience. In India, the pathway to becoming a radiologist is well-defined, but it also demands a commitment to continuous learning and adaptability, especially with the rapid advancements in technology like AI in radiology.
The journey to becoming a radiologist in India involves multiple stages, starting from completing your basic medical degree to further specialization in radiology. Whether you’re just beginning your educational journey or are already in the medical field considering radiology, I’ll walk you through the key steps, qualifications, and exams you’ll need to take to make your way into this exciting field.
Education and Entrance Exams
To become a radiologist, you’ll first need to complete a medical degree (MBBS) and then pursue specialized training in radiology.
Here’s a breakdown of the education required to become a radiologist in India:
The Role of AI in Radiology Education
With the growing influence of AI in medical imaging, future radiologists will need to be adept at working with AI-powered tools and platforms. Radiology students today are increasingly being exposed to AI technologies as part of their training. According to a recent study by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), 50% of radiologists believe that AI tools will play a major role in their practice in the coming years, assisting with tasks like diagnosing diseases from imaging and reducing human error.
Having a solid foundation in these technologies will not only enhance your career but also make you more competitive in the job market.
Pathways for Career Progression in Radiology
Once you’ve completed your initial medical degree and training, your radiology career can branch out in several directions, including:
- Clinical Radiology: Focusing on interpreting images and providing diagnostic services.
- Interventional Radiology: Using imaging techniques to guide minimally invasive surgeries.
- Radiology Research and Academia: Engaging in cutting-edge research or teaching the next generation of radiologists.
The scope for career advancement in radiology is substantial, especially with the advent of AI and other medical innovations. Whether you wish to specialize, become a consultant, or teach, there are multiple opportunities to grow in this field.
Necessary Soft Skills and Technical Abilities for Radiologists
Becoming a successful radiologist isn’t just about mastering medical imaging techniques or learning to interpret X-rays and MRIs. It’s also about developing the right set of soft skills and technical abilities to ensure that you can perform your job efficiently, communicate effectively, and work as part of a multidisciplinary team.
As a radiologist, you’ll interact with healthcare professionals across different specialties, such as surgeons, oncologists, and neurologists, as well as patients. In my experience, the most successful radiologists possess a combination of communication skills, attention to detail, and emotional intelligence, alongside their technical expertise.
According to a study by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), radiologists who are skilled in these areas are better at providing comprehensive care and ensuring patient safety. So, whether you’re just starting out or looking to further your career in radiology, it’s important to develop both soft skills and technical expertise to excel in this field.
Let’s take a closer look at what you need to succeed in radiology.
Soft Skills
Communication Skills
In radiology, clear communication is essential — not only when discussing findings with physicians but also when conveying complex information to patients, especially when explaining procedures or results. A radiologist needs to translate technical jargon into language that patients can understand. This helps reduce patient anxiety, builds trust, and enhances the overall care experience.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
In radiology, you’re often faced with complex cases where split-second decisions can make all the difference. Having strong problem-solving skills means you can quickly analyze imaging results, identify abnormalities, and provide accurate diagnoses that will inform treatment. Your ability to think critically and make judgments based on your findings will be key to your success as a radiologist.
Attention to Detail
Radiology is a field where the smallest detail can have significant implications for patient care. A radiologist must have an exceptional eye for detail when reviewing medical images. Missing even a small tumor or fracture can lead to serious consequences. Attention to detail, combined with thoroughness, is essential for minimizing diagnostic errors.
Time Management
Radiologists often have heavy caseloads, with dozens or even hundreds of images to review daily. Effective time management is critical, especially when balancing routine scans with emergency or urgent cases. Good time management helps ensure that all tasks — from diagnosing patients to consulting with other healthcare professionals — are completed promptly without compromising quality.
Technical Abilities
Medical Imaging Technology Expertise
Radiologists need to be experts in operating and interpreting a range of medical imaging technologies, including X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. Familiarity with the latest advancements, such as AI-assisted imaging tools, is increasingly important in providing accurate and timely diagnoses. For instance, AI tools now assist in detecting conditions like breast cancer and lung disease, helping radiologists improve diagnostic accuracy.
Diagnostic Imaging Interpretation
The core of radiology is interpreting images to detect and diagnose medical conditions. This requires an in-depth understanding of anatomy, pathology, and imaging techniques. Radiologists must be able to differentiate between normal and abnormal images and provide clear, actionable reports for other healthcare providers. Further certifications, like Certified Radiology Technician (CRT) or Board Certification in Radiology, can enhance your expertise in this area.
Radiology Informatics and EHR Systems
With the increasing reliance on digital imaging and health records, knowledge of radiology informatics is becoming a must-have skill. Radiologists need to be proficient in using Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) to store and share images. These technologies streamline workflow, but knowing how to navigate them effectively is crucial for maintaining accurate patient records and collaborating with other healthcare professionals.
Quality Control and Safety
A radiologist’s role also involves ensuring the safety of patients during imaging procedures. This includes making sure radiation levels are kept to a minimum, following proper protocols for image acquisition, and ensuring the maintenance of medical equipment. Radiologists also monitor the quality of the images to ensure they are of sufficient clarity for accurate diagnosis. Certification options like Certified Radiology Safety Officer can bolster your credentials in this area.
AI and Machine Learning in Radiology
AI is increasingly being integrated into radiology practices. Radiologists should be comfortable working with AI-powered tools that assist in image analysis, help predict disease progression, and even automate routine tasks.
Medical Equipment Operation and Maintenance
Radiologists must understand how to operate and maintain advanced imaging equipment, including CT scanners, MRIs, and ultrasound machines. Technical knowledge is key, not only for ensuring that images are captured correctly but also for troubleshooting and resolving any issues that may arise with the equipment.
Career Progression and Growth Opportunities in Radiology
The field of radiology offers a diverse and rewarding career path with numerous opportunities for growth. From interpreting diagnostic images to playing a crucial role in guiding treatment plans, radiologists are in high demand across hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers.
Let’s break down the typical career progression in radiology, along with opportunities to advance your career and further your expertise.
Typical Career Path in Radiology
Entry-Level Roles (0-2 years)
- Positions: Junior Radiologist, Radiology Resident: Entry-level radiologists primarily focus on learning the ropes of the profession by reviewing images under supervision, assisting senior radiologists, and gaining hands-on experience with various imaging modalities. Radiology residents are often involved in daily clinical work and participate in rounds with other specialists.
- Growth Tip: Gaining experience with various imaging technologies (such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasound) is key at this stage. It’s also important to focus on developing strong diagnostic skills. During this period, some radiologists may pursue certifications like Certified Radiology Technologist (CRT) to build their credentials.
Mid-Level Roles (2-5 years)
- Positions: Consultant Radiologist, Senior Radiologist, Interventional Radiologist
- Focus: Radiologists in these roles take on more complex cases, interpreting images independently and providing diagnostic insights for physicians and patients. Some radiologists may specialize in interventional procedures, using imaging techniques to guide minimally invasive surgeries. Mid-level radiologists also start to focus on specific areas of radiology, such as musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, or oncologic imaging.
- Growth Tip: At this stage, pursuing advanced certifications in specialized areas like Neuroradiology, Pediatric Radiology, or Interventional Radiology can greatly enhance your career prospects. Keeping up with advancements in AI and how it’s reshaping the field of radiology will also give you an edge.
Specialist Roles (5-10 years)
- Positions: Lead Radiologist, Senior Interventional Radiologist, Radiology Consultant
- Focus: Specialist radiologists have a deep focus on specific subfields, like oncologic radiology, neuroimaging, or musculoskeletal radiology. They may also supervise junior radiologists and provide expert opinions in complex cases. These roles often involve working closely with multidisciplinary teams to design treatment plans based on imaging results.
Growth Tip: If you wish to further specialize, consider pursuing fellowships in areas like Pediatric Radiology, Neuroradiology, or Cardiovascular Radiology. Developing expertise in the integration of AI-powered diagnostic tools will be a huge asset for these roles.
Growth Opportunities in Radiology with the Rise of AI
AI is transforming the field of radiology, and embracing these advancements will be crucial to your career growth. AI can help radiologists by automating routine tasks, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, and allowing radiologists to focus on more complex cases. Radiologists who adapt to AI tools and continue to integrate them into their workflow will likely see career progression opportunities, as they will be more efficient and effective in their diagnoses.
Educational and Certification Growth Opportunities
As radiology continues to evolve, radiologists should focus on continuous learning through specialized courses, certifications, and fellowships. Here are a few key options to consider:
- Fellowships: Specializations such as Interventional Radiology, Pediatric Radiology, and Neuroradiology can open doors to advanced roles and responsibilities.
- AI and Machine Learning Courses: Understanding AI and its applications in radiology will become increasingly important as technology reshapes the industry. Many universities and medical institutions now offer certifications and courses in radiology AI.
Research and Academia: For those looking to take on academic or research roles, pursuing a Ph.D. or contributing to cutting-edge radiology research can lead to opportunities to influence the future of the field.
Salary Expectations and ROI in Radiology
A common question many aspiring radiologists and their families ask is, “Will a radiology career provide financial stability and career growth?” The answer is a resounding yes.
Return on Investment (ROI)
A radiology career in India is a strong financial investment, particularly given the growing demand for skilled radiologists and the increasing role of medical imaging in patient care.
In ROI you should include the cost of MBBS and in ROT the time taken to do MBBS
Education Costs (approximate) in Per Annum
- MD Radiology (PG): ₹8 lakh to ₹52 lakh (MBBS cost inclusive)
Earnings Potential:
- Entry-Level Salary for MD Radiology: ₹7 lakh to ₹36 lakh

Radiologists in private institutions or running their own practices can see even higher salaries, particularly if they specialize in areas like oncology or interventional radiology.
Return on Time (ROT) in Radiology
Radiology is a profession that offers a clear and structured pathway, but it also demands patience and commitment, particularly when considering the time invested in education and training. Below is a breakdown of the time required to pursue a career in radiology:
Education Duration in Radiology
MBBS (Undergraduate):
- Duration: 5.5 years
- To begin a career in radiology, aspiring radiologists must first complete an MBBS degree, which typically takes 5.5 years.
MD in Radiology (Postgraduate):
- Duration: 3 years
- After completing MBBS, aspiring radiologists need to pursue a 3-year postgraduate degree (MD) in Radiology.
Thus, the total time investment to become a radiologist — including both MBBS and MD in Radiology — is approximately 8.5 years.
Return on Time (ROT) in Terms of Earnings:
A radiologist can begin expecting to earn immediately after completing their MD in Radiology, typically within 1 year of completing their postgraduate degree.
Break-even Point:
The time it takes to secure a job depends on the institution and location, but most radiologists (MD) start earning within 6 months after completing their postgraduate degree. On the other hand, those with a DNB in Radiology take 1 year to start earning after completing the degree.
Fast-Track Options:
Radiologists can choose to specialize early in their careers, for instance, in interventional radiology, where they can begin performing minimally invasive procedures with image guidance.
As AI continues to reshape the field, radiologists who are quick to adapt to these technologies will be in high demand, leading to faster career advancement and higher earning potential.

Future Prospects: The Next 20–30 Years in Radiology
The field of radiology is rapidly evolving, shaped by technological advancements, the growing demand for diagnostic imaging, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). Over the next 20–30 years, radiology will undergo significant transformations, opening up new opportunities and challenges for radiologists.
According to a report by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), the role of radiologists will continue to expand, especially with the rise of AI-assisted imaging, telemedicine, and automated diagnostic tools. AI and machine learning are already making their mark in radiology. AI algorithms are now being developed to assist in detecting everything from tumors and fractures to more subtle diseases like Alzheimer’s and heart conditions.
According to the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA), the implementation of AI in radiology could significantly reduce the time it takes to process images, making healthcare more efficient and accessible. As technology continues to advance, new areas of specialization in radiology will emerge.
Radiologists with expertise in AI, machine learning, and even robotics will be in high demand. Specializations such as interventional radiology, which uses imaging techniques to guide minimally invasive procedures, are also expected to see significant growth. Additionally, pediatric radiology, neuroradiology, and oncologic radiology will remain in high demand, particularly as more focus is placed on early detection and personalized medicine.
Imaging technologies will be essential in monitoring long-term conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative diseases, which require continuous tracking and intervention. Radiologists with expertise in managing chronic conditions, particularly those with knowledge of AI-enhanced diagnostic tools, will be at the forefront of managing long-term care, collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive treatment plans.
Conclusion
Radiologists are crucial to the healthcare system, guiding treatment plans and helping doctors make life-saving decisions based on their expertise in medical imaging.
The rewards go far beyond financial gain. Radiologists play an essential role in patient care, working alongside healthcare teams to improve lives through accurate diagnostics and cutting-edge technology.
For parents, supporting your child’s pursuit of radiology means investing in a profession that not only offers financial stability but also contributes significantly to the betterment of society. For students, radiology is a chance to combine technical expertise, healthcare, and problem-solving skills in a dynamic and impactful career.
I hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the radiology profession and the opportunities it offers. If you’re still uncertain about which specialization or pathway in radiology best suits your goals, don’t hesitate to reach out — I’d be happy to help you navigate your journey toward a successful and fulfilling career in radiology.