Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
When I first explored the world of dentistry, I realized something beautiful — dentists don’t just “fix teeth.” They restore confidence, bring back smiles, remove pain, and help people feel better about themselves. A dentist’s touch can transform someone’s self-esteem, appearance, and overall health. If you find yourself fascinated by smiles, oral care, aesthetics, and the science behind human anatomy, then a dentist career in India could be your ideal path.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through how to become a dentist in India with absolute clarity — from Class 12 to BDS, internships, licensing, specialization, and the different careers you can build. By the end, you’ll have a complete dental career roadmap to decide whether this profession aligns with your strengths, compassion, and long-term goals.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Dentist
Dentistry is far more dynamic than simply “drilling and filling.” Depending on your specialization and practice setting — clinic, hospital, cosmetic studio, community, or academic field — your daily responsibilities can look very different.

Key Responsibilities of a Dentist
Dentists are responsible for improving oral health, relieving pain, boosting aesthetics, and preventing long-term dental issues. Their core duties include:
- Diagnosing dental diseases through oral examinations, X-rays, and diagnostic tools.
- Performing treatments like fillings, extractions, root canal therapy, crowns, bridges, and dentures.
- Delivering preventive care — scaling, polishing, fluoride treatment, sealants, and oral hygiene education.
- Designing and executing smile makeover treatments such as veneers, whitening, and cosmetic procedures.
- Performing minor oral surgeries and assisting oral surgeons in complex procedures.
- Managing pediatric dental cases, orthodontic alignment, and geriatric oral care.
- Educating patients on oral hygiene, lifestyle habits, preventive practices, and post-treatment care.
- Maintaining accurate dental records, radiographs, treatment notes, and case documentation.
- Staying updated with evolving technologies like digital dentistry, lasers, aligners, and CAD-CAM systems.
- Collaborating with dental hygienists, lab technicians, orthodontists, surgeons, and healthcare teams.
Work Environment of a Dentist
A dentist’s work environment changes based on where they practice. Common setups include:
1. Dental Clinics / Private Practice
- Most common setup for dentists in India
- Greater independence in treatment decisions
- Flexible working hours depending on patient flow
- Higher income potential in the long run
- Opportunity to build long-term patient relationships
2. Hospitals (Government or Private)
- Steady patient inflow
- Structured schedules but may require emergency duties
- Exposure to complex oral, maxillofacial, and trauma cases
- Chances to collaborate with multi-specialty teams
3. Cosmetic & Aesthetic Dentistry Studios
- Focus on smile design, veneers, whitening, and aligners
- High use of modern tech: scanners, smile analysis software, lasers
- More upscale environment and aesthetic-driven clientele
4. Teaching Hospitals / Dental Colleges
- Combination of patient care + teaching BDS/MDS students
- Participation in research, presentations, and dentistry workshops
5. Community Health Centres / Rural Healthcare
- Managing broad oral health needs
- Delivering preventive and outreach programs
- Involvement in government oral health missions
6. Corporate Dental Chains
- Standardized treatment protocols
- High patient volume
- Opportunities for managerial or leadership roles

Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications
Choosing the right education pathway is the foundation of how to become a dentist. As a student, you may feel confused with entrances, eligibility, or specializations — but once you understand the structure, everything becomes simpler.
Below is a clear, organized table covering every major step in the dental profession in India.
Complete Education & Exam Roadmap for Becoming a Dentist
Typical Skills & Personal Qualities You’ll Need
When you choose dentistry, you’re not just choosing a profession — you’re choosing a role that blends science, precision, artistry, and empathy. As you begin your journey, you’ll realize dentistry shapes your personality just as much as your clinical expertise.
Here are the essential skills and qualities needed to thrive in the dental profession in India:
Technical Skills Every Dentist Must Build
These are the scientific and clinical abilities that form the backbone of dental practice:
- Strong foundation in Biology, Chemistry, and Basic Medical Sciences
Crucial for understanding oral structures, diseases, and treatment procedures. - Excellent hand–eye coordination and precision
Dentistry involves micro-movements inside a tiny working area — accuracy is everything. - Aesthetic sense for cosmetic and restorative treatments
Especially important for smile design, veneers, crowns, and aesthetic dentistry. - Ability to perform detailed, demanding procedures with steady hands
Whether it’s a root canal or a surgical extraction, technical dexterity matters daily.
Soft Skills That Shape a Successful Dentist
These qualities turn a good dentist into a trusted one:
- Patience, empathy, and understanding of patient anxiety
Many patients fear dental visits — compassion builds trust. - Strong communication and counselling abilities
Explaining procedures, calming nerves, and discussing treatment plans require clarity. - Ability to work calmly in stressful situations
Dental emergencies and complex procedures need composure. - Emotional resilience
Handling long procedures, difficult cases, or anxious patients can be mentally taxing. - Discipline, dedication, and a problem-solving mindset
Dentistry rewards professionals who are consistent, meticulous, and solution-driven. - Lifelong learning mindset
Essential because treatment protocols, materials, and technologies update continuously.

Career Progression: From BDS Graduate to Dental Specialist & Beyond
Your dental journey doesn’t end when you finish BDS — it’s actually the beginning. Most students eventually wonder, “Should I specialise? Open a clinic? Join a hospital?” Understanding your long-term growth path will help you plan wisely.
1. Career Path After BDS (Step-by-Step Progression)
a) BDS Graduate (Fresh Dentist)
- Start your compulsory internship
- Get exposure to all departments — conservative dentistry, prosthodontics, pedodontics, orthodontics, OMR, surgery, etc.
- Receive your State Dental Council registration
b) Choose Between – 4 Main Career Routes
Clinical Practice
- Work in dental clinics or open your own practice
- Build a patient base, gain experience, and start cosmetic or specialty services
Postgraduate Studies (MDS / Specialization)
- Prepare for NEET-MDS for fields like orthodontics, endodontics, prosthodontics, oral surgery, pedodontics, etc.
Research & Public Health
- Join dental research labs, ICMR programs, MPH, or public health projects
Non-Clinical Dental Careers
- Dental insurance
- Medical writing
- Dental equipment companies
- Teaching
- Hospital administration
c) Specialization Route
If you choose MDS, here’s your path:
- MDS (3 years) – Specialist training
- Senior Residency – Advanced clinical exposure
- Fellowships – Implantology, lasers, esthetics, endodontics
- Super-specialty roles depending on the department
d) Practice as a Specialist
- Consultant or senior dentist in clinics/hospitals
- Start specialty-based private practice
- Join cosmetic centers or orthodontic chains
- Build your brand as a smile design expert
2. Growth Opportunities at Each Stage
a) After BDS
- Junior Dentist
- Associate Dentist in clinics
- Dental Surgeon in hospitals
- Public Health Dentist
- Clinical Research roles
- Teaching positions in dental colleges
- Jobs in corporate dental chains
b) After MDS (Specialist Level)
- Specialist dentist (Orthodontist, Endodontist, Prosthodontist, etc.)
- Senior consultant
- Faculty in dental colleges
- Cosmetic dentistry expert
- Aligners specialist
c) Advanced Opportunities After Fellowships / Experience
- Head of department
- Cosmetic studio owner
- Implantologist with premium services
- Forensic odontologist
- International career through global exams
d) Alternative Growth Tracks
- Dental entrepreneurship (clinic chains, labs, tech startups)
- Tele-dentistry platforms
- Hospital management and quality control
- Roles in dental equipment and pharma companies
Dentistry evolves constantly — and the more you learn, the more you grow.
Salary Expectations
Understanding your earning potential helps you plan your future better. In dentistry, income grows steadily with experience, specialization, patient base, and clinic location.
Average Salary Structure for Dentists in India
- After BDS (General Dentist)
- Entry-level: ₹3–6 lakhs per year
- With 2–4 years experience: ₹6–12 lakhs per year
- Government Dental Surgeon: ₹8–14 lakhs per year + allowances
- After MDS (Specialized Dentist)
- Junior Specialist: ₹12–20 lakhs per year
- Senior Specialist: ₹20–35 lakhs per year
- Cosmetic/Aesthetic dentistry: ₹25–50 lakhs+ annually
- Private Practice
- Established private practice can easily earn ₹20 lakhs to ₹80 lakhs+ yearly
- Premium cosmetic clinics may exceed ₹1 crore+ annually
- Alternative Careers
- Dental Research: ₹6–20 lakhs
- Teaching roles: ₹6–15 lakhs
- Dental companies/Corporate roles: ₹8–20 lakhs
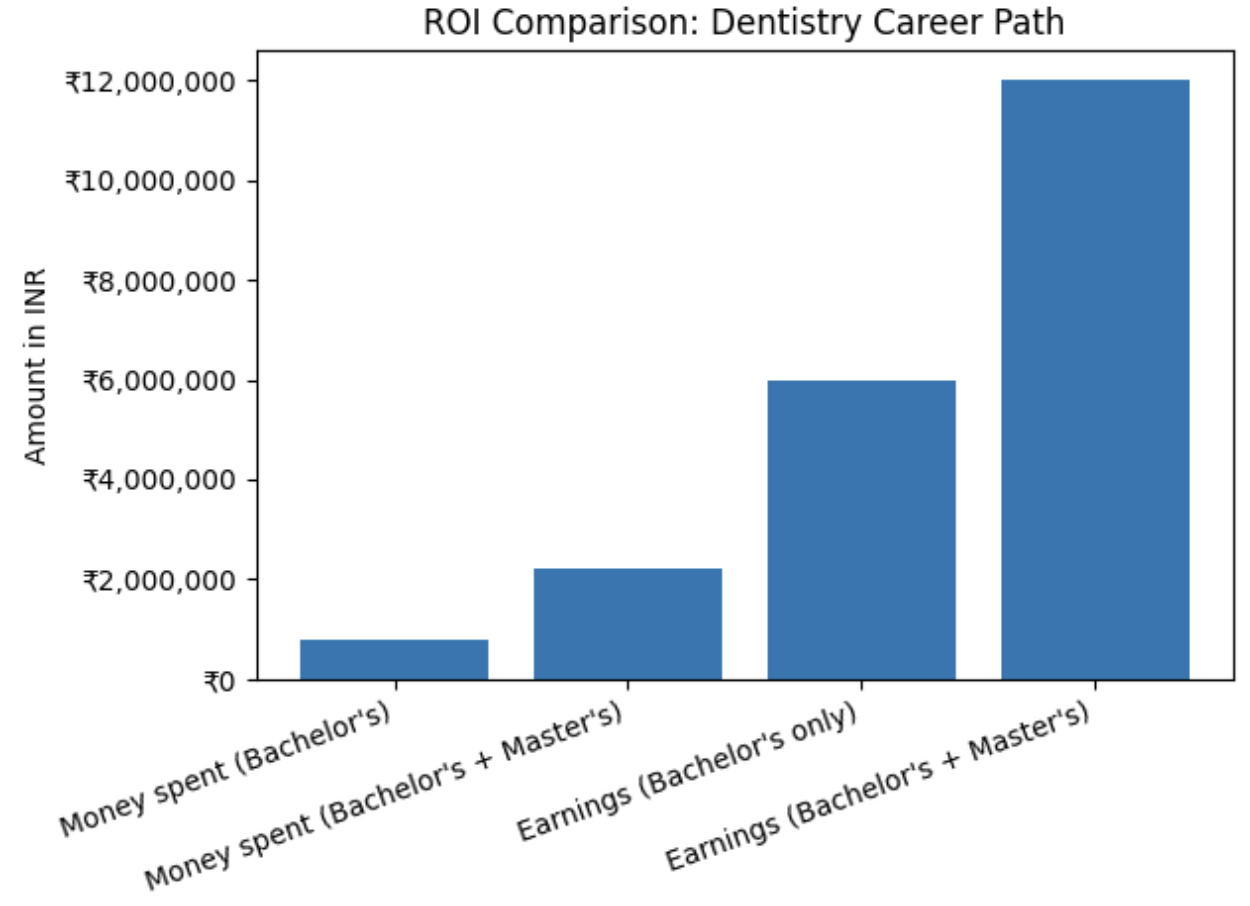
Understanding ROI and ROT in a Dental Career
ROI – Return on Investment
ROI tells you whether the money invested (BDS fees, materials, clinic setup) gives proportional financial returns.
- BDS fees range from ₹3 lakhs to ₹30+ lakhs
- MDS fees may go higher depending on specialization
- Clinic setup costs: ₹5 lakhs to ₹25 lakhs
- Most dentists achieve ROI within 5–10 years, depending on specialization and practice growth.
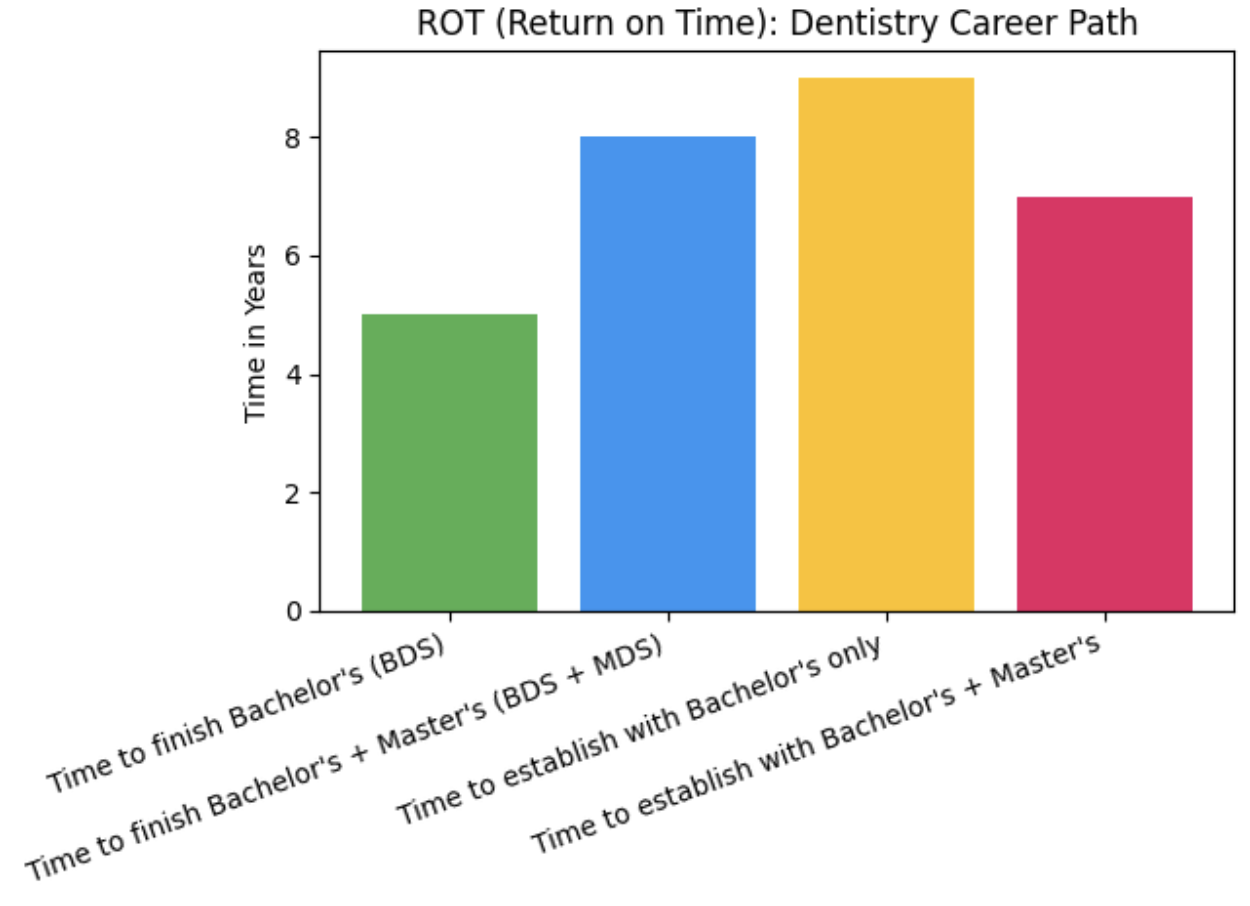
ROT – Return on Time
ROT evaluates whether the time you invest gives long-term rewards.
Dentistry requires both academic commitment and gradual trust-building. Here’s the realistic timeline most parents don’t hear about:
- 5 years of BDS (4 years academics + 1-year compulsory internship)
- 2–3 years of clinical experience to gain confidence, refine procedures, and build patient relationships
- 3–5 years to establish a stable independent practice (if the student chooses private practice)
So typically, a dentist becomes professionally established in 6–8 years, and achieves a strong, steady practice in 8–10 years, depending on specialization, city, and career path.
Conclusion: Is a Career as a Dentist Right for You?
Becoming a dentist is more than a profession — it’s a commitment to improving smiles, boosting confidence, and enhancing quality of life. If you enjoy science, precision, aesthetics, communication, and helping people, the dental profession in India can be deeply rewarding.
Ensure you’re ready with the right subjects (PCB in Class 12), prepared for NEET-UG, and committed to the 5-year BDS journey. With passion, discipline, and the right guidance, you can build a successful dental career full of purpose and opportunities.
Connect with our expert counsellors at NextMovez today and get a personalized dental career roadmap based on your strengths and goals.
Let’s turn your dream of becoming a dentist into a confident, well-planned reality.
Resources and References
- Dental Council of India (DCI) – Guidelines, BDS/MDS regulations, college approvals
https://dciindia.gov.in - National Medical Commission (NMC) – NEET UG notifications, counselling rules
https://www.nmc.org.in - Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) – Health workforce and policy updates
https://www.mohfw.gov.in - National Testing Agency (NTA) – NEET UG exam patterns, dates, and syllabus
https://nta.ac.in