Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
When I first began guiding students toward teaching careers, I noticed something important — government teachers don’t just teach subjects; they shape generations. They build discipline, curiosity, confidence, and values that last a lifetime. Behind every successful professional is often a dedicated teacher who believed in them early on.
If you enjoy explaining concepts, mentoring young minds, contributing to nation-building, and seeking a career with stability, respect, and long-term security, then this path may be right for you. In this blog, I’ll walk you through how to become a government teacher in India with complete clarity — from eligibility after Class 12 or graduation to TET exams, recruitment processes, job roles, salary structure, and career growth.
By the end, you’ll have a clear government teacher exam pathway to decide whether this profession aligns with your aptitude, patience, and long-term goals.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Government Teacher
Teaching in a government school is far more than delivering lessons. It involves academic instruction, student mentoring, administrative responsibilities, and community impact.
Key Responsibilities of a Government Teacher
Government teachers play a crucial role in shaping foundational learning and holistic development. Their core responsibilities include:
- Teaching prescribed subjects as per NCERT / State Board curriculum
- Preparing lesson plans aligned with academic calendars
- Conducting assessments, exams, and evaluations
- Maintaining student records, attendance, and progress reports
- Identifying learning gaps and supporting slow learners
- Encouraging discipline, ethics, and social values
- Participating in school activities, assemblies, and training programs
- Implementing government education schemes and policies
- Communicating with parents and guardians
- Attending professional development and teacher training workshops

Work Environment of a Government Teacher
A government teacher’s work environment depends on the level and location of posting.
- Primary & Upper Primary Schools (Classes 1–8)
- Focus on foundational literacy and numeracy
- Strong emphasis on child psychology and engagement
- Teaching multiple subjects (especially in primary classes)
- Secondary & Senior Secondary Schools (Classes 9–12)
- Subject-specialist teaching
- Exam-oriented curriculum and board preparation
- Academic mentoring and career guidance role
- Urban Government Schools
- Better infrastructure and access to resources
- Higher student diversity
- Rural & Remote Area Schools
- Wider social impact and community engagement
- Opportunity to contribute to inclusive education
- Residential / Model Government Schools (KVs, NVs)
- Structured systems and national-level exposure
- Competitive recruitment and transfers across India
Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications
Understanding test exam eligibility and academic requirements early helps avoid confusion later. The pathway varies based on the level you want to teach.
Below is a clear, structured roadmap.
Complete Education & Exam Roadmap for Becoming a Government Teacher
Typical Skills & Personal Qualities You’ll Need
Teaching is a profession of knowledge, patience, empathy, and responsibility. Over time, it shapes both your intellect and character.
Technical Skills Every Government Teacher Must Build
- Strong subject knowledge aligned with school syllabus
- Lesson planning and classroom management skills
- Assessment and evaluation techniques
- Basic digital teaching tools (smart boards, e-content)
- Understanding of child development and pedagogy
- Familiarity with NEP 2020 and education policies
Soft Skills That Shape a Successful Government Teacher
- Patience, empathy, and emotional intelligence
- Clear communication and explanation skills
- Ability to manage diverse classrooms
- Adaptability to different student learning styles
- Discipline, consistency, and accountability
- Problem-solving mindset
- Commitment to continuous professional development
Career Progression: From Aspiring Teacher to Senior Educator
Becoming a government teacher is not the end — it’s the beginning of a long, respected career.
- Career Path After Qualification (Step-by-Step Progression)
- a) Aspiring Teacher Stage
- Complete D.El.Ed or B.Ed
- Meet ctet qualification requirements or State TET norms
- Clear CTET / State TET
- b) Recruitment & Appointment Stage
- Apply for state or central teacher recruitment
- Clear written exams and document verification
- Receive posting and complete probation
- c) Permanent Government Teacher
- Regular salary, benefits, and job security
- Periodic transfers and promotions
- Growth Opportunities at Each Stage
- a) Entry-Level
- Primary Teacher (PRT)
- Trained Graduate Teacher (TGT)
- b) Mid-Level
- Post Graduate Teacher (PGT)
- Subject Head / Senior Teacher
- c) Senior Roles
- Head of Department
- Vice Principal
- Principal
- Alternative & Advanced Growth Tracks
- Educational administration roles
- DIET / SCERT faculty
- Curriculum designer
- Education policy and training roles
- Government education inspection services
Teaching careers offer structured growth with dignity and stability.

Salary Expectations
Government teaching salaries are standardized and increase with experience.
Average Salary Structure for Government Teachers in India
- Primary Teacher (PRT)
- ₹25,000 – ₹35,000 per month
- Trained Graduate Teacher (TGT)
- ₹35,000 – ₹45,000 per month
- Post Graduate Teacher (PGT)
- ₹45,000 – ₹60,000 per month
- Senior Roles (Principal)
- ₹70,000 – ₹1,00,000+ per month
Additional benefits include DA, HRA, pension, medical benefits, and paid leaves.
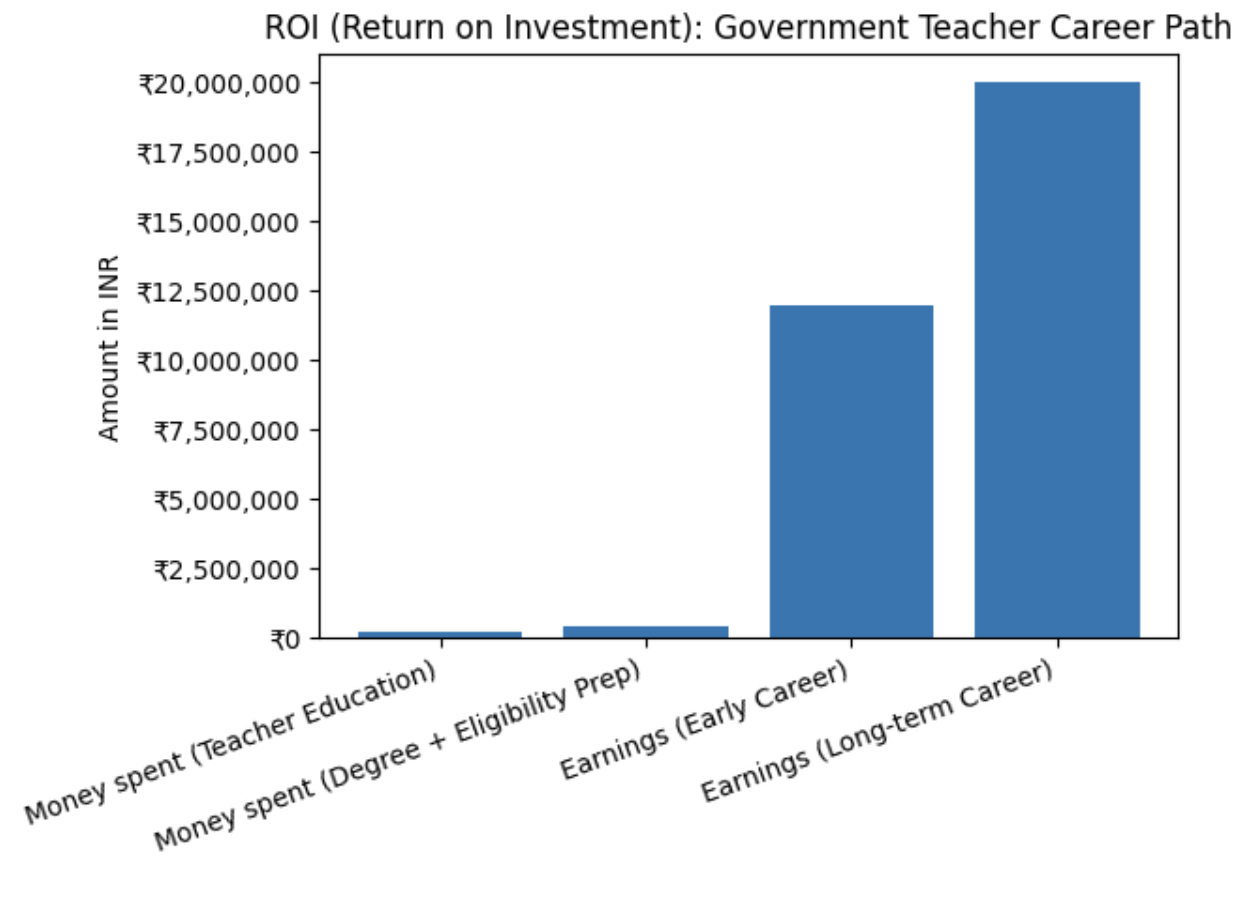
Understanding ROI and ROT in a Government Teaching Career
ROI – Return on Investment
- Education cost: ₹1–4 lakhs (D.El.Ed / B.Ed)
- Minimal financial risk
- Strong ROI due to stable income and benefits
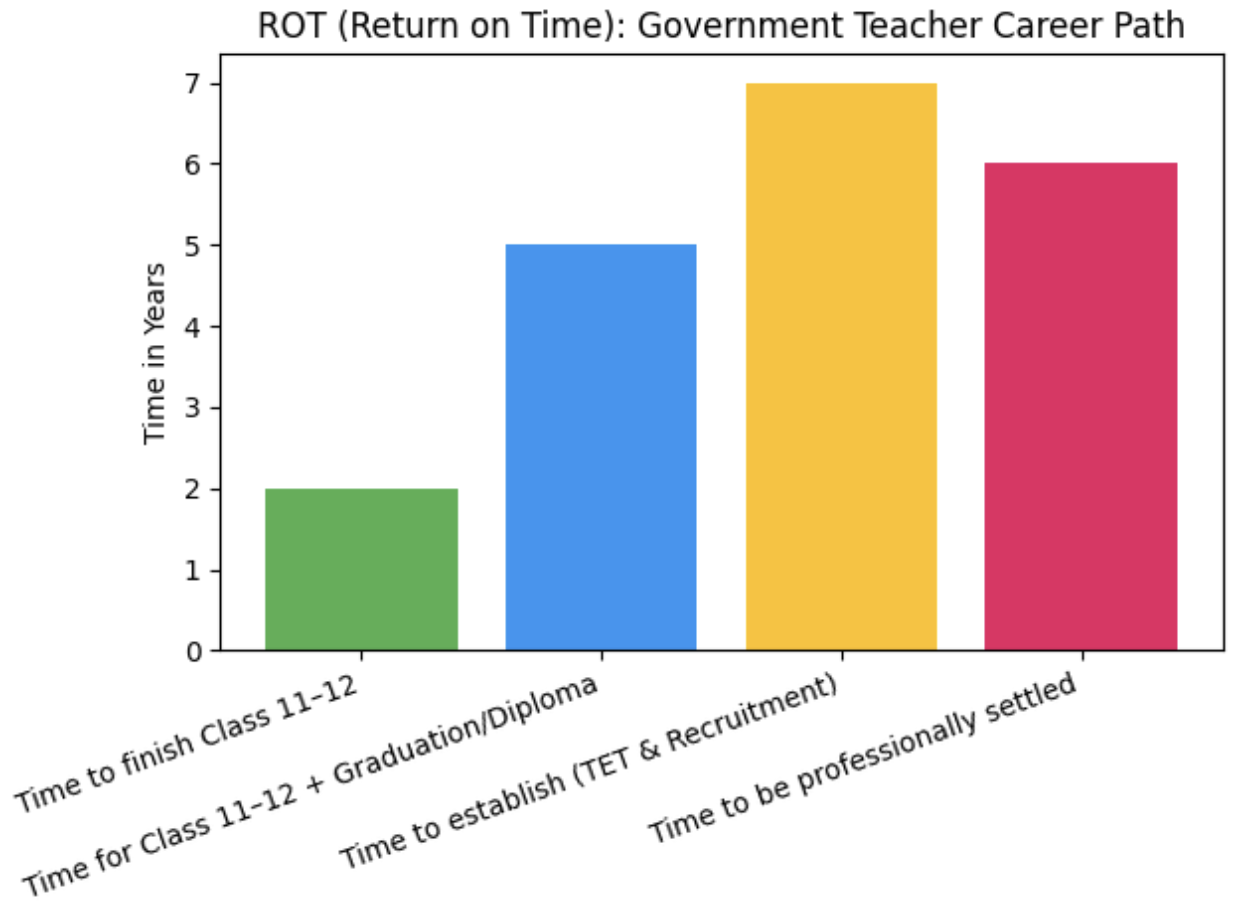
ROT – Return on Time
- 2 years (Class 11–12)
- 2–3 years (Graduation / Diploma)
- 1–2 years for TET & recruitment
Most candidates become professionally settled within 5–6 years, with lifelong job security.
Conclusion: Is Becoming a Government Teacher Right for You?
If you are passionate about teaching, value stability, and want to contribute meaningfully to society, then this path can be deeply fulfilling. Understanding how to become a government teacher, meeting tet exam eligibility, and following the right government teacher exam pathway can make your journey smooth and confident.
With the right preparation, patience, and guidance, teaching becomes not just a job — but a respected lifelong profession.
Connect with our expert counsellors at NextMovez today and get a personalized teaching career roadmap tailored to your strengths and goals.
Let’s turn your passion for teaching into a confident, well-planned reality.
Resources and References
- CBSE – CTET notifications and syllabus
https://ctet.nic.in - Ministry of Education – School education policies
https://www.education.gov.in - State Education Boards – TET & recruitment updates
- National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) – Teacher education standards
https://ncte.gov.in