Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
When I first considered the path to medicine, I was struck by something — the power of healing isn’t just about knowledge or technology, but about empathy, trust, and responsibility. Physicians don’t just treat bodies; they comfort minds, restore hope, and stand as pillars of support for patients and families. If you find yourself drawn to caring for people, helping when they’re vulnerable, and making a real difference in lives — then a career as a physician could be your calling.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through how to become a physician in India step by step — from clearing Class 12 and entrance exams, to earning your MBBS, possibly specializing, and building a meaningful and impactful medical career. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to decide if the medical path resonates with your aspirations and strengths.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Physician

Being a physician is far broader than just “treating patients.” Depending on your speciality and setting — hospital, clinic, community health, teaching or research — your day could look very different.
Key Responsibilities of a Physician
Physicians play a central role in diagnosing, treating, and improving patient health. Their responsibilities extend far beyond hospital rounds and prescriptions. Key duties include:
- Diagnosing illnesses and evaluating symptoms through clinical examination, patient history, and medical tests.
- Prescribing treatments and medications, and adjusting plans based on the patient’s response.
- Monitoring patient progress and making informed decisions in critical or evolving situations.
- Providing counselling and emotional support to patients and families, especially during complex or chronic illnesses.
- Collaborating with nurses, specialists, and healthcare teams for coordinated and effective patient care.
- Educating patients about preventive health, lifestyle changes, follow-up routines, and recovery guidelines.
- Maintaining accurate medical records, reports, and case documentation for legal and professional compliance.
- Participating in public health screenings, awareness camps, or community outreach initiatives when required.
- Engaging in continuous medical learning, attending seminars, workshops, or training to stay updated with evolving medical practices.
Work Environment of a Physician
The work environment for physicians varies significantly depending on their specialization, place of practice, and career stage. Physicians may work in:
Hospitals (Government or Private)
- High patient inflow, fast-paced care settings, emergency situations.
- Rotational shifts, night duties, and on-call responsibilities.
- Opportunities for teamwork, advanced equipment usage, and skill development.
Clinics or Private Practice
- More predictable routine and long-term relationships with patients.
- Higher autonomy in decision-making and patient management.
- Flexible schedules, depending on the doctor’s setup and patient load.
Community Health Centres / Rural Healthcare
- Direct work with underserved communities.
- Broader general practice responsibilities.
- Often linked to public health programs and preventive care.
Teaching Hospitals & Medical Colleges
- Dual role: treating patients + teaching medical students.
- Involvement in academic discussions, research, and training.
Research Institutes / Public Health Organisations
- Focus on disease patterns, clinical trials, epidemiology, policy-making.
- Work is more analytical, data-driven, and structured.
Corporate Health, Telemedicine & Digital Healthcare
- Increasingly popular due to digital transformation in healthcare.
- Virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and technology-driven patient follow-ups.
- More structured hours and reduced physical strain compared to hospital shifts.
Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications

Choosing the right educational pathway is one of the most defining steps in your journey to becoming a physician. As a student, you may feel overwhelmed with exams, eligibility rules, and multiple career entry points — but once you understand the structure clearly, planning becomes much easier.
Below is a clear, organized breakdown of every major exam and pathway, helping you decide what fits your goals best.
Essential Technical Skills You Need to Become a Physician
Even before you wear the white coat, certain technical skills form the backbone of your journey as a doctor. These skills ensure you can handle the scientific, analytical, and communication demands of medical training and medical practice.
- Diagnostic Acumen: Assessing symptoms, analyzing lab results, reading scans, and forming accurate diagnoses.
- Treatment Administration: Prescribing medications correctly, performing injections, setting IVs, and managing acute care (e.g., airway management).
- Medical Procedures: Proficiency in basic tasks like drawing blood, wound care, and specialized procedures depending on their field (e.g., surgery, dermatology).
- Medical Equipment: Competence in using diagnostic tools, monitoring devices, and biomedical equipment.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Efficiently navigating and documenting in EHR systems for patient records and charting.
- Medical Informatics: Understanding data analysis, medical statistics, and applying evidence-based medicine.
Personal Qualities That Shape a Great Doctor
Beyond academics, medicine is a human-centric profession. These qualities define how well a doctor can connect, comfort, and care for people.
1. Empathy, Patience & Compassion
To truly support patients through pain, fear, and uncertainty, doctors must be able to listen deeply and understand their emotions.
2. Emotional Resilience
Medical school and clinical practice can be stressful and draining. Handling emergencies, long hours, and emotional situations requires strong mental and emotional stability.
3. Discipline & Commitment
From rigorous study schedules to years of clinical training, becoming a doctor demands unwavering dedication and consistent discipline.
Career Progression: From Fresh MBBS to Specialist & Beyond
Your journey as a doctor doesn’t end with an MBBS degree — in fact, that’s where it truly begins. Every medical student eventually reaches a point where they wonder, “What comes next? Should I pursue specialization? Which path gives me the most growth?” Understanding your career progression early helps you make confident decisions, avoid unnecessary confusion, and plan a future that aligns with your strengths and passions. Below is a clear breakdown of how your career can evolve from a new MBBS graduate to a seasoned specialist or even a leader in the healthcare ecosystem.
1. Career Path After MBBS (Step-by-Step Progression)
- a) Choose Between
- Clinical Practice
- Work as a general physician/medical officer in hospitals, clinics, or government health services.
- Postgraduate Studies (Specialization)
- Prepare for NEET-PG, INI-CET, or pursue overseas PG.
- Research or Public Health Pathways
- Join ICMR, WHO projects, MPH programs, or academic research labs.
- Non-Clinical Careers
- Medical writing, healthcare management, pharmaceutical roles, medico-legal roles, and more.
- b) Specialization Route
If you choose to specialize, here’s how your journey flows:
- MD/MS (3 years) – Foundation for becoming a specialist
- Senior Residency (3 years) – Advanced hands-on training
- c) Practice as a Specialist
- Become a consultant/specialist in hospitals.
- Start private practice or join corporate healthcare systems.
2. Growth Opportunities at Each Stage
- a) After MD/MS (Specialist Level)
- Consultant in hospitals
- Specialist roles in multispecialty and super-specialty centers
- Teaching faculty in medical colleges
- Opportunities in telemedicine and digital health platforms
- Leadership roles in hospital departments
- b) After DM/MCh (Super-Specialist Level)
- Senior consultant or lead specialist
- Head of department (HoD) roles
- Positions in top-tier institutions like AIIMS, PGI, NIMHANS
- International fellowships and global career opportunities
- Private practice with higher earning potential
- c) Alternative Growth Tracks
- Healthcare Administration: Hospital management, quality control, medical director roles
- Research & Academics: Principal investigator, professor, medical scientist
- Entrepreneurship: Clinics, diagnostic centers, med-tech startups
- Global Health: WHO, UNICEF, UN health missions
Medicine is rarely a “static job.” With time, specialisation, continuous learning, and perhaps interest in research or public health — it becomes a long, evolving career full of opportunities.
Salary Expectations
Understanding how much you can earn as a doctor isn’t just about numbers — it’s about planning your future with clarity. Many students and parents want to know whether the years of effort, long study hours, and financial investment in medical education will pay off. The truth is, your income as a physician grows steadily with experience, specialization, and the type of healthcare setting you choose.
Here’s a simple, realistic breakdown to help you understand what to expect at each stage.
Average Salary Structure for Physicians in India
Note: Salaries vary based on city, hospital type (government/private/corporate), specialization, and experience.
- After MD/MS (Specialist)
- Junior Consultant: ₹12–18 lakhs per year
- Mid-level Specialist: ₹18–30 lakhs per year
- Private Practice (popular fields like Dermatology/Orthopedics/Pediatrics): Can cross ₹30–50 lakhs annually
- After DM/MCh (Super-Specialist)
- Consultant (Corporate Hospitals): ₹35–60 lakhs per year
- Lead Consultant / HoD: ₹60 lakhs–₹1 crore+ per year
- Private/Own Practice: Can exceed ₹1 crore yearly depending on location and reputation
- Non-Clinical & Alternative Careers
- Clinical Research / Pharma: ₹8–20 lakhs
- Hospital Administration: ₹10–25 lakhs
- Health-tech / Telemedicine: ₹6–18 lakhs
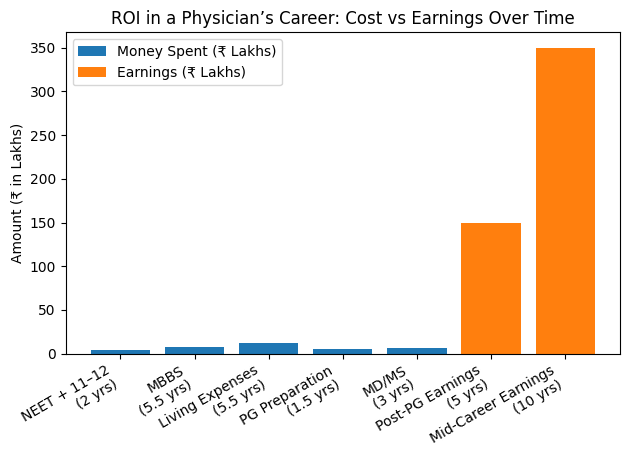
Understanding ROI and ROT in a Medical Career
When parents ask about ROI in medicine, what they really want to know is:
“How much will we spend from Class 11 until specialization—and when will earnings cross that amount?”
Let’s break it down clearly.
1. Total Money Spent on Becoming a Physician (Approx.)
Total Investment Range
- Government route: ₹18–30 lakhs
Private route (MBBS + PG): ₹80 lakhs – ₹1.2 crore+
2. Earnings After Medical Education
Doctors do not earn significantly during training. Real income begins after an MBBS + internship, and increases sharply after specialization.
3. When Does ROI Actually Break Even?
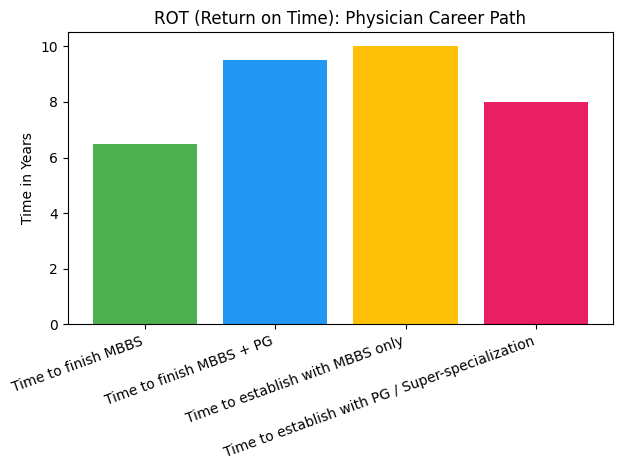
What is ROT (Return on Time)?
ROT answers a different but equally important question:
“Are the years my child invests worth the long-term rewards?”
Medicine requires a long learning runway:
MBBS (5.5 years) + Internship (1 year) + PG (3 years) + Super-specialty (3 years)
That’s 8–12+ years before a doctor reaches stable earning levels.
Why ROT is crucial:
- The profession offers unmatched stability, respect, and lifelong relevance.
- Every year invested compounds into career longevity—many doctors practice well into their 70s.
- High job security and deep social impact make the time investment emotionally rewarding.
Conclusion: Is a Career as a Physician Right for You?
Becoming a physician is more than a career choice — it’s a life commitment. If you’re driven by compassion, responsibility, dedication, and a desire to help people, medicine can be a deeply fulfilling path. The journey demands hard work, persistence, and continuous learning — but the rewards go beyond just salary. A physician can touch lives, contribute to society, and build a respected career that evolves with time, specialization, and service.
If you — or someone you guide — are serious about becoming a doctor: ensure you have the academic readiness (PCB in Class 12), are prepared for competition (NEET-UG), and are ready for years of study + service. With sincerity and perseverance, you can transform from a student full of hopes to a doctor committed to healing and service.
Connect with our expert counsellors at NextMovez today and get a personalized roadmap for your medical career journey.
Let’s turn your dream of becoming a doctor into a confident, well-planned reality.
Resources & References
- National Medical Commission Annual Report 2023 — Doctor Registration Data
https://www.nmc.org.in - Ministry of Health — India’s Doctor-Population Ratio Report
https://www.mohfw.gov.in - NMC Medical College Data 2023
https://www.nmc.org.in/information-desk/for-students-to-study-in-india/ - OECD & WHO Global Health Workforce Statistics
https://www.who.int/data - EY India – Telemedicine Market Report
https://www.ey.com/en_in - Lancet Digital Health – AI in Clinical Diagnosis
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landig - ICMR India Diabetes Study 2023
https://www.icmr.gov.in - NITI Aayog Healthcare Workforce Report
https://www.niti.gov.in - IBEF Healthcare Sector Report
https://www.ibef.org