Blog written by Indu R Eswarappa, Career Coach & Education Change-Maker
Nursing is one of the most rewarding professions in the world — yet it often doesn’t get the recognition it deserves. Nurses are the unsung heroes, providing care, comfort, and crucial support to patients in every healthcare setting. If you’re asking, “How can I become a nurse?” — you’re not alone. More people than ever are considering this noble profession. Whether it’s caring for the elderly, helping women through childbirth, or being at the frontline in emergency rooms, the nursing profession offers numerous ways to make a real difference in people’s lives.
In my opinion, nursing isn’t just about giving medications or performing medical procedures. It’s about being there for patients, offering emotional support, and playing an integral part in their recovery. Nurses are the backbone of the healthcare system, and they play a crucial role in both patient care and the healthcare team. In India, the nursing profession is growing rapidly, and there are numerous pathways to enter the field, depending on your interests and educational background.
In this blog, I’ll guide you through the steps to become a nurse, from the necessary qualifications and exams to the key skills and career opportunities available in the nursing profession in India. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to pursue a nursing career and what it takes to succeed.
Key Responsibilities and Work Environment of a Nurse
From providing direct patient care in the morning to assisting in surgeries or managing critical care units in the afternoon, no two days are ever the same for a nurse. Nursing is a dynamic and demanding profession, where each day presents new challenges and the opportunity to make a meaningful impact on people’s lives.
According to Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science, as a nurse, your responsibilities extend far beyond just administering medications or monitoring vital signs. You become a crucial part of a healthcare team, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care while maintaining their dignity and comfort. Let me walk you through the key responsibilities of a nurse and the type of environment you can expect to work in.
Key Responsibilities of a Nurse
Patient Care and Monitoring
Whether it’s monitoring vital signs, administering medications, or ensuring proper nutrition and hygiene, nurses are hands-on caregivers in every healthcare setting. Nurses work closely with doctors, specialists, and other healthcare professionals to create and implement care plans tailored to each patient’s needs.
Assisting in Medical Procedures
Nurses often assist doctors and surgeons during medical procedures, ranging from routine examinations to life-saving surgeries. Their role in maintaining sterile environments, preparing medical tools, and offering emotional support to patients is vital.
Patient Education and Counseling
Nurses help patients understand their medical conditions, explain treatment plans, and guide them through recovery. This aspect of nursing involves communication skills and empathy, as patients may be facing emotional challenges in addition to physical ones.
Medication Administration and Management
A key responsibility of a nurse is ensuring that patients receive the correct medications at the right times. This requires a keen understanding of pharmacology, careful attention to dosage, and close monitoring of patients for any adverse reactions.
Specialization
As you grow in your nursing career, you may choose to specialize in areas such as pediatrics, oncology, cardiology, or intensive care. Specializing allows you to gain expertise in a specific field and can open doors to advanced roles such as Nurse Practitioners or Nurse Educators.
Work Environment for Nurses
Whether you work in a hospital, a clinic, a nursing home, or a community healthcare center, the atmosphere will depend on your specific role and the needs of your patients. Here’s what you can expect:
Hospitals and Clinical Settings
Whether in emergency rooms, intensive care units, or general wards, nurses in hospitals are often at the heart of patient care, working long shifts and sometimes under high-stress conditions.
Outpatient Clinics and Healthcare Centers
Nurses in outpatient settings tend to have more regular hours and deal with patients on a less critical level. This may include routine check-ups, health assessments, or vaccination clinics. While the pace may be slower than in hospitals, the responsibility remains high.
Home Care and Community Health
Nurses working in home care visit patients at their homes to provide care, typically to elderly or chronically ill individuals. These nurses must be highly independent, as they manage a range of tasks alone while maintaining patient care.
Workplace Flexibility and Challenges
Whether it’s shift work in a busy hospital or a more regular schedule in a clinic, nursing offers flexibility to suit different career preferences. However, the emotional and physical demands of the job are significant. Nurses are often working in high-stress environments, dealing with difficult patients, and handling emergency situations.
Nursing is a multifaceted career that offers opportunities to work in various settings, from hospitals and clinics to home care and research. Nurses need to be adaptable, compassionate, and ready for new challenges each day, with a direct impact on the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
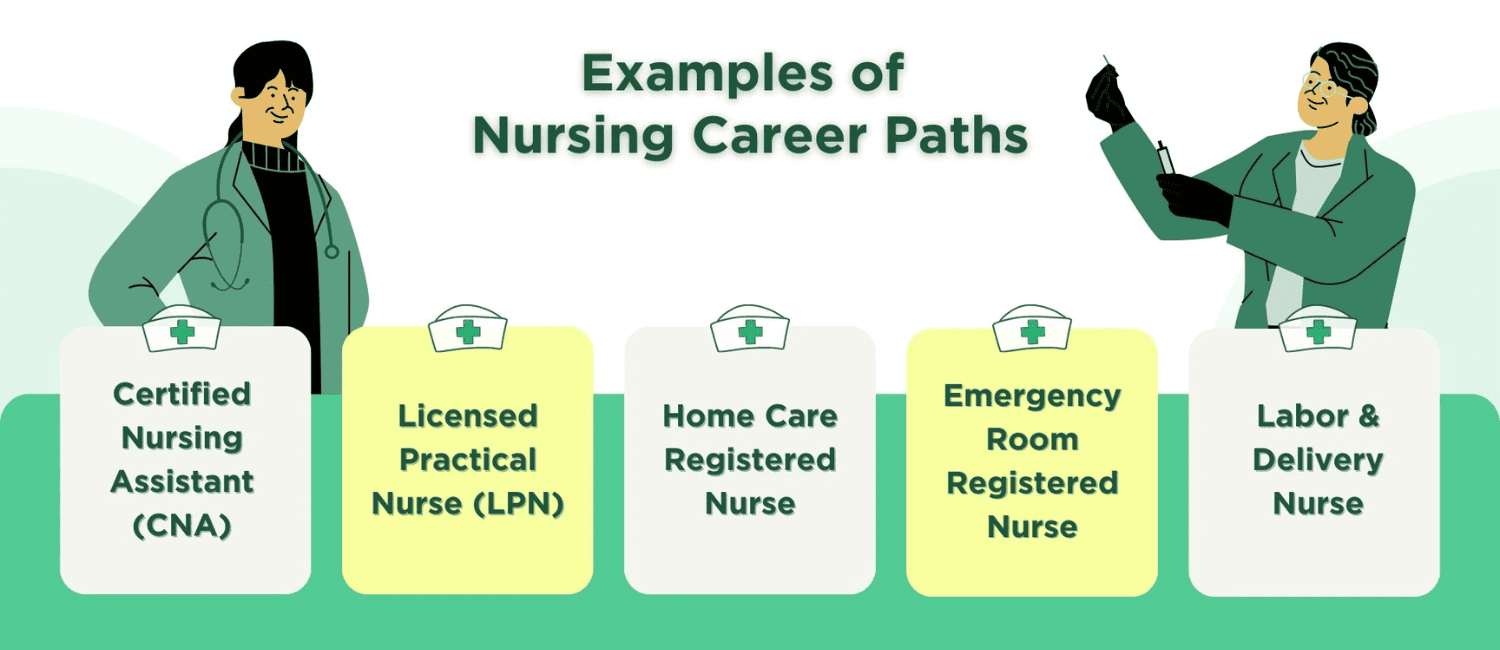
Educational Pathways and Required Qualifications
Becoming a successful nurse in India requires not only academic knowledge but also practical experience, continuous learning, and a deep understanding of patient care.
The journey to becoming a nurse in India combines formal education, entrance exams, professional certifications, and hands-on clinical experience.
According to the Indian Nursing Council‘s eligibility criteria, the ideal time to start pursuing a career in nursing is after completing 10+2. There are multiple routes, such as ANM, GNM, and B.Sc Nursing, to become a nurse, which we will discuss shortly. Whether you’re a student just beginning or someone considering a career change later in life, here’s a clear roadmap to guide your path to becoming a nurse.
Education and Entrance Exams
To become a nurse, you’ll need to follow an academic pathway that combines theory, practical training, and certification. Here’s an overview of the essential courses and qualifications you’ll need at various levels.
Necessary Soft Skills and Technical Abilities
Think about the best nurse you’ve ever encountered — what made them stand out? It probably wasn’t just their medical knowledge, but their ability to communicate effectively with patients, manage stressful situations, and show empathy and care. Nurses who excel in these areas often build strong relationships with patients, which can positively impact their recovery and overall well-being.
Furthermore, technical skills are just as crucial. According to Hospital and Healthcare Management, nurses must adhere to the “Five Rights” of medication administration — the right patient, the right drug, the right dose, the right route, and the right time. This practice is vital for ensuring medication accuracy and preventing errors that could lead to severe complications.
To excel in the nursing profession in India, you’ll need a combination of both soft skills and technical abilities. These skills will not only help you build trust with patients and their families, but also equip you to navigate complex healthcare challenges. Let’s take a closer look at the skills you’ll need to thrive in this career.
Soft Skills
Communication Skills
Effective communication is key in nursing. Whether you’re providing instructions to patients, collaborating with doctors, or interacting with families, clear communication can make all the difference in patient care.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Nurses often deal with patients in vulnerable, emotional situations. High emotional intelligence helps you empathize with patients, comfort them during difficult times, and build a trusting relationship that can positively affect their recovery process.
Problem-Solving
Every patient presents a unique challenge. As a nurse, you’ll need to think critically, assess situations quickly, and make decisions that are in the best interest of the patient.
Attention to Detail
In nursing, small errors can have big consequences. Nurses must have a keen eye for detail when administering medication, recording patient information, or monitoring vital signs. Even the smallest mistake can affect a patient’s health, so nurses need to be meticulous in every aspect of their work.
Time Management
Time management is a crucial skill for nurses, as it allows them to prioritize their duties, manage patient needs, and ensure that every task is completed efficiently — from administering treatments to ensuring proper documentation.
Technical Abilities
Patient Care Management and Monitoring:
A nurse’s ability to monitor patients’ vital signs, recognize symptoms of distress, and respond quickly to changes in a patient’s condition is crucial. Nurses need to be proficient in using medical technology to track patient health and provide appropriate interventions. Certification option: Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Certification or Basic Life Support (BLS) for emergency care.
Nursing Documentation and Record Keeping:
Nurses must be able to document patient care effectively, ensuring all records are up-to-date and accurate. This includes entering patient histories, documenting symptoms, and noting medication administration. Certification option: Certified Electronic Health Record Specialist (CEHRS).
Medical Equipment Operation:
Understanding how to operate, calibrate, and troubleshoot medical devices is essential for patient safety. Technical knowledge of these tools can ensure that they are used correctly in critical care situations. Certification option: Certified Clinical Research Coordinator (CCRC) to gain further expertise in medical research equipment handling.
Nursing Informatics:
From managing patient data using Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems to telemedicine applications, technological proficiency is a growing requirement in nursing. Certification option: Certified Informatics Nurse (RN-BC).

Career Progression and Growth Opportunities in Nursing
Nursing offers an exciting array of opportunities, from bedside care to administrative roles, education, and advanced practice. Additionally, as healthcare technology continues to evolve, nurses now have more ways to enhance their impact and stay at the forefront of patient care.
Typical Career Path in Nursing
Clinical Nursing Roles
Entry-Level Roles (0-2 years)
Positions: Registered Nurse (RN), Staff Nurse
Focus: Providing direct patient care, administering medications, and documenting patient progress. Entry-level nurses often work in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
Growth Tip: Gaining experience in specialized areas such as pediatrics or critical care will help you build expertise and move into higher-level roles.
Mid-Level Roles (2-5 years)
Positions: Charge Nurse, Nurse Supervisor, Clinical Nurse Specialist
Focus: Supervising junior nurses, managing patient care plans, and coordinating between departments. Nurses in these roles also play a crucial part in educating patients and families.
Growth Tip: Earning certifications in areas like Critical Care Nursing (CCRN) or Pediatric Nursing (CPN) will expand your career options.
Specialist Roles (5-10 years)
Positions: Nurse Practitioner (NP), Nurse Educator, Nurse Manager
Focus: Nurses in these roles often have advanced responsibilities, such as diagnosing and treating patients, managing nursing teams, or teaching future nurses. Nurse Practitioners, for instance, can prescribe medications and perform diagnostic tests.
Growth Tip: Consider pursuing a Master of Science in Nursing (M.Sc Nursing) or specialized certifications to enhance your qualifications for advanced roles.
Senior Roles (10+ years)
Positions: Nurse Administrator, Nurse Director, Clinical Nurse Leader
Focus: Overseeing nursing operations within healthcare facilities, setting policies, and leading teams of nurses. These nurses are often involved in high-level decision-making and strategic planning.
Growth Tip: Earning leadership certifications or an advanced degree in healthcare administration can open doors to executive roles in nursing.
Salary Expectations and ROI in Nursing
A common question many aspiring nurses and their families ask is, “Will a nursing career provide financial stability and career growth?” The answer is a resounding yes.
Return on Investment (ROI)
A nursing career in India is a strong financial investment, particularly given the growing demand for healthcare professionals. While the cost of nursing education can vary, it is generally more affordable than other healthcare-related programs like medical school, yet it offers competitive salaries and growth potential.
Nursing education also provides opportunities for hands-on clinical experience, which is a valuable asset when starting your career.
Education Costs (approximate)
- B.Sc Nursing Program (UG): ₹2 lakh to ₹5 lakh
- M.Sc Nursing Program (PG): ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh
These costs can vary depending on the institution. Top nursing colleges and universities, such as those affiliated with AIIMS or Christian Medical College, may charge higher fees but often offer scholarships and financial aid opportunities.
Earnings Potential:
- Entry-Level Salary for B.Sc Nursing: ₹2.5 lakh to ₹4.5 lakh per annum
- Entry-Level Salary for M.Sc Nursing (PG): ₹4 lakh to ₹6 lakh per annum
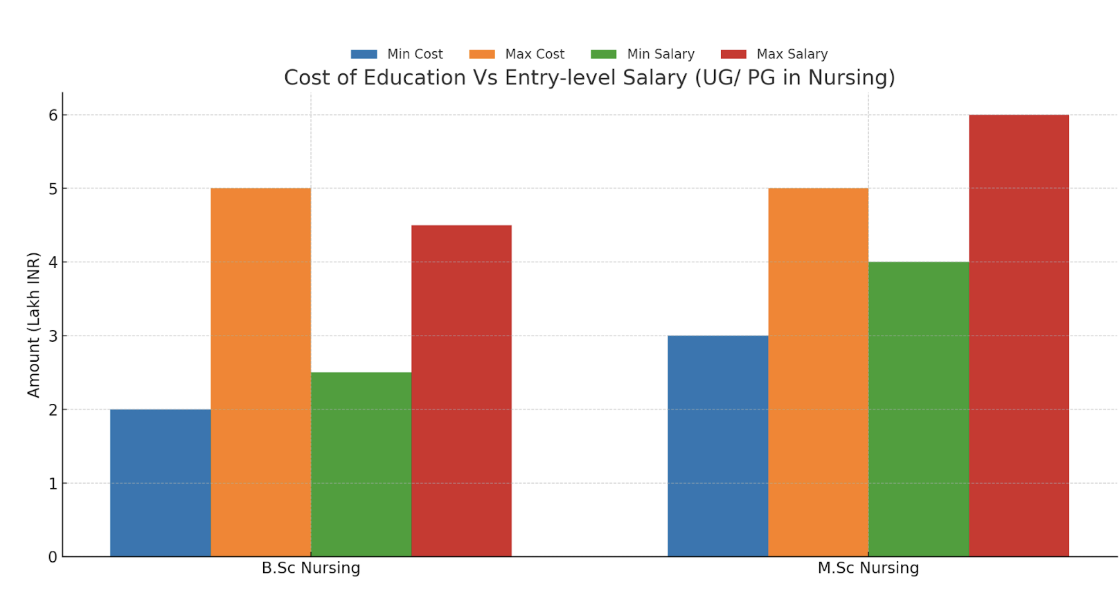
Data Source: Propelld.Com Nursing Fees & Entry-level Salary
As you progress in your nursing career, the potential for earnings increases. Nurses who specialize in high-demand areas like ICU nursing, anesthesia, or emergency care can earn even more.
Return on Time (ROT) in Nursing
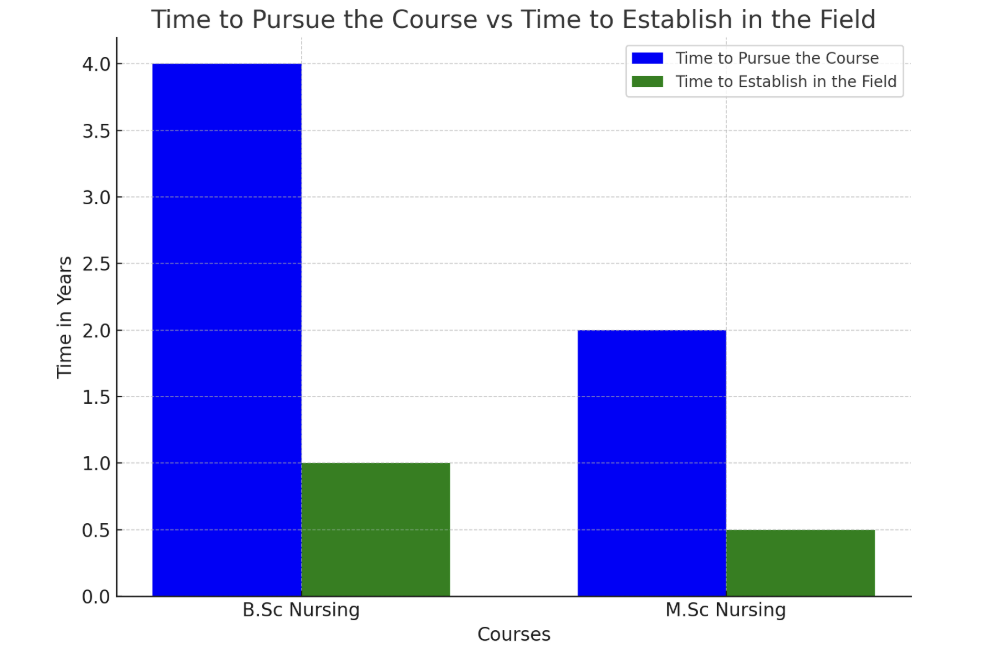
Let’s talk about time, because for many aspiring nurses, how long it takes to start earning is just as important as the salary expectations. Nursing is a profession that offers both a quick path to entry-level roles and a rewarding, long-term career.Education Duration:
- B.Sc Nursing Program (UG): 4 years
- M.Sc Nursing Program (PG): 2 years
Break-even Point:
In my experience, most nursing graduates begin working almost immediately after completing their education. With a B.Sc Nursing degree, many new nurses start working in hospitals or clinics soon after graduation, often securing jobs within six months.For those with an M.Sc Nursing degree, positions are usually secured more quickly due to their specialization, although the hiring process can still take up to six months in some cases.
Fast-Track Options:
For those looking to advance more quickly in their careers, there are fast-track options. Nurses can specialize in high-demand areas such as ICU, emergency care, or anesthesia, which not only lead to higher salaries but can also shorten the time to career growth.
Future Prospects: The Next 20–30 Years in Nursing
The nursing profession is undergoing significant changes, shaped by advancements in healthcare technology, an aging population, and evolving patient care needs. According to the NCBI Research Report, over the next 20–30 years, we will see major transformations in the way healthcare is delivered and the opportunities available to nurses.
According to the WHO Blog on EHR (Electronic Health Records), as technology continues to advance, tools such as telemedicine, robotic-assisted surgery, and electronic health records (EHRs) are becoming integral to nursing practice. These innovations will enable nurses to focus more on direct patient care, while also streamlining administrative tasks, improving efficiency, and contributing to better patient outcomes.
Specializations such as nursing informatics, telehealth nursing, and geriatric care are expected to see increased demand as the healthcare landscape evolves.
With an aging population in India and the global rise in chronic conditions, nurses with expertise in these fields will play a crucial role. They will be instrumental in managing long-term care and supporting the healthcare system.
The future of nursing is dynamic, with opportunities for nurses to take on leadership roles, become educators, or specialize in advanced practice roles.
Conclusion
Becoming a nurse isn’t just about caring for patients — it’s about becoming a beacon of compassion, healing, and support. From administering medications and managing complex care plans to providing emotional support, nurses play a critical role in the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
The journey to becoming a nurse requires dedication, empathy, and a deep commitment to patient care. The rewards extend far beyond a paycheck. Nurses are not only building a career, but also establishing trust, purpose, and influence that can positively impact lives.
For parents, supporting your child’s pursuit of nursing means investing in a respected profession that offers stability, respect, and a chance to make a real difference. For students, it’s an opportunity to combine science, compassion, and leadership in a career that truly matters.
I hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the nursing profession and its diverse opportunities. If you’re still unsure which nursing path or specialization aligns best with your goals, don’t hesitate to reach out — I’d be happy to help you navigate your journey toward a fulfilling nursing career.